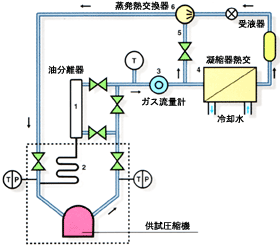
 |
Refrigerant vapor flowmeter method
1.Small quantities of discharged oil and refrigerant vapor are separated by the oil separator.
2.Separated oil is returned to the specimen air compressor.
3.The flow rate of refrigerant vapor is measured by a gas flowmeter.
4.About one-fifth of the discharged refrigerant vapor flows into the heat exchanger of the condenser, where it is chilled and liquefied.
5.The remaining discharged refrigerant vapor passes through the bypass line and fed directly into the heat exchanger.
6.They are then combined in the heat exchanger of the evaporator before being returned to the specimen air compressor. |
Briefly, the refrigerant vapor flowmeter method is designed to test the refrigerating capacities of various types of independent air compressor employed in package air conditioners, room air conditioners, automotive air conditioners, refrigerators, etc., by measuring the rate at which discharged refrigerant vapor flows through the circuits. Although there are several measurement methods, the evaporator calorimeter method (secondary fluid calorimeter method) and the refrigerant liquid flowmeter method have been widely employed so far.
Satake leads the field in Japan in developing and employing air compressor calorimeters using the refrigerant vapor flowmeter method.
In due consideration of environmental protection , the CALOACE 21 does not use freon gas, which is necessary in the case of the secondary fluid calorimeter method. The CALOACE 21 is an air compressor calorimeter which uses the latest method to achieve greater energy conservation and more reliable reproducibility.
Compressor Calorimeter CALOACE 21 (Refrigerant vapor flowmeter method)
- An air compressor calorimeter using the refrigerant vapor flowmeter method is designed to test the refrigerating capacities of air compressors by measuring the rate at which of discharged refrigerant vapor flows through the circuits(according to JIS B 8606 Test methods for refrigeration purpose air compressors).
- Use of secondary fluid is not required, and the amount of refrigerant passing through the circuit is reduced to approximately 40% of that in conventional types.
Comparison of the secondary fluid calorimeter and refrigerant vapor flowmeter methods [Energy and space saving]
Refrigerant vapor flowmeter methods are kept low electric power consumption.
| Secondary fluid calorimeter methods |
|
Refrigerant vapor flowmeter methods |
| Used.(heater: 10kW) |
Heat exchanger of the evaporator |
Used.(heater: not used.) |
| Used.(heater: 1.2kW) |
Super-cooling heat exchanger |
Not used |
| Used.(heater: 3.7kW) |
Refrigerator |
Used.(0.75kW) |
| Used.(heater: 18kW) |
Water tank heater |
Used.(2kW) |
| About 2.5 to 3.0 kg |
Amount of refrigerant used
(in the case of the R-22) |
About 1.2 to 1.7kg |
Approximately 3.22㎡
(incorporating the water tank)
Approximately 0.6㎡
(separately installed refrigerator) |
Installation space required for the system equipment(Cycle equipment) |
Approximately 2㎡
(incorporating the water tank and refrigerator) |
*The above data are those of 2HP class air compressor calorimeters.
*Data for the refrigerant vapor flowmeter method are taken with standard air compressor calorimeters.
 |
New Product
Oil Rate Measuring Device
(Patent registered)
Oil discharge characteristics under various compressor conditions are measured in real time, accurately and speedily. |